Mode C and Mode D
Last update:2025-04-21 15:33:42
Topics
- Authentication URL Structure
- How to Configure Mode C and Mode D
- Authentication Key($ourkey)
- Time Format
- Signature Calculation Algorithm
- Signature Calculation Parameters
- Signature Parameter Name
- Timestamp Parameter Name
- Valid Time (Seconds)
- Key and Time Positions Interchangeable
- Quick Verify if the URL Authentication Configuration is Correct
This document provides a detailed explanation of Authentication Modes C and D, along with instructions on how to use them.
Authentication URL Structure
Authentication Modes C and D allow you to embed authentication information as request parameters in the URL. Here are the URL formats for these two modes:
Authentication Mode C
http://domain/uri?key=signature&time=timestamp
Authentication Mode D
http://domain/uri?time=timestamp&key=signature
In these URL structures, key represents the authentication signature, and time is the timestamp when the URL was generated. These authentication parameters are added to the URL, and the CDN edge server verifies them to determine whether to serve the requested content. Similar to Authentication Modes A and B, once configured, the order of key and time is fixed, and client requests must include these parameters in the specified order, or the CDN edge server will reject the request.
In Modes C and D,
keyandtimeare request parameters whose names can be customized. For instructions on how to modify the names of these authentication parameters, refer to the Key Parameter Name and Time Parameter Name sections.
Explanation of Fields in the Authentication URL
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| domain | The domain you have added for the CDN. |
| uri | The actual path of the URL requesting content from the CDN. For instance, if the original request URL is http://cdnetworks.com/browse/index.html, then the uri would be /browse/index.html. If the request URL includes query parameters (e.g., /browse/index.html?user=123), the uri should only contain the path of the requested object, excluding the query string |
| time | The timestamp in the authentication URL, indicating when the URL was generated. The CDN edge server uses this timestamp to determine if the URL is still valid. If the current time surpasses the valid period of the URL, the content will not be served. The time value must follow the predetermined timestamp format; otherwise, authentication will fail. For the supported time stamp formats, see the Time Format section of this document. |
| key | The encrypted signature used for authentication verification, typically generated by combining the time stamp, an encryption key (ourkey), and the actual path (uri). For details on how this authentication parameter is computed, refer to the Signature Calculation Parameters section of this document. |
How the Authentication Works on CDN Edge Servers
When the CDN edge server receives a request, it first verifies whether the timestamp time in the authentication URL has expired:
- If the timestamp
time, plus the valid duration, is less than the current time, the URL is considered expired, access is denied, and an HTTP 403 error is returned. - Conversely, if the timestamp
time, plus the valid duration, meets or exceeds the current time current time, the CDN edge server will consider the URL valid. It then calculates the expected authentication signature(key) expected for the request URL and compares it with the signature in the request. If they match, authentication succeeds, and server fulfills the content request; otherwise, the request is denied, and an HTTP 403 error is returned.
How to Configure Mode C and Mode D
In the Authentication Modes settings, select Mode C or Mode D as needed. The following sections explain the purpose and method for each configuration field.
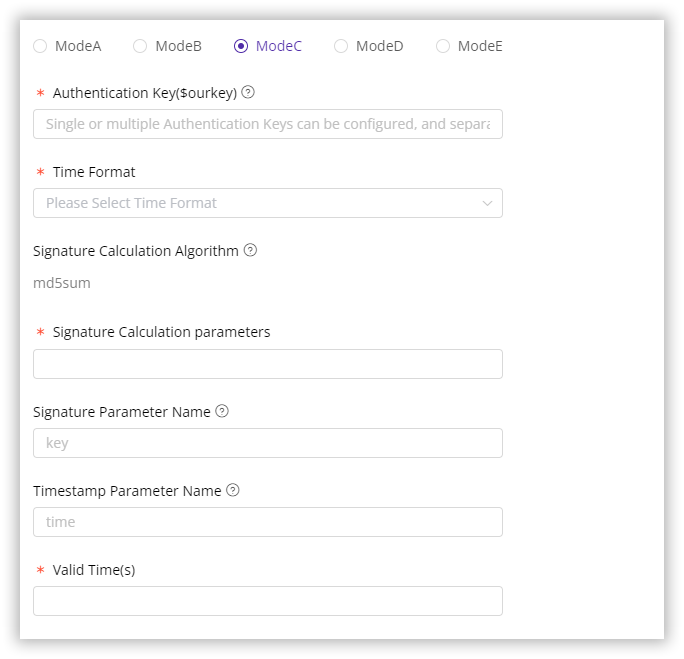
Authentication Key($ourkey)
The Authentication Key ($ourkey) is a unique string used to generate the authentication signature key in the URL. This ourkey, shared only between you and our CDN servers, enhances security by making the authentication parameters difficult for unauthorized parties to crack. You can set multiple ourkey values in the console, separated by semicolons (;).
When multiple ourkey values are configured, the CDN edge server will use them in order to authenticate requests. If the first ourkey fails, the server will try the next one, and so on, until a valid key is found or all keys fail validation.
Time Format
For constructing an authentication URL, the time field offers five optional formats to accommodate diverse requirements:
| Timestamp Format | Description |
|---|---|
| Decimal Unix Timestamp | E.g., 1586338211 represents April 8, 2020, 17:30:11 UTC. |
| Hexadecimal Unix Timestamp | E.g., 5e8e2463 represents 1586338211 in hexadecimal. |
| UNIX timestamps in milliseconds | E.g., 1586338211000 represents the same point in time. |
| YYYYMMDDHHMMSS | E.g., 20200408173011 represents April 8, 2020, 17:30:11. |
| YYYYMMDDHHMM | E.g., 202004081730 represents April 8, 2020, at 17:30. |
Signature Calculation Algorithm
The signature key is generated using an encryption algorithm. By default, we use the MD5 algorithm. If you need a different encryption algorithm for enhanced security, please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Signature Calculation Parameters
To generate the authentication signature key, you can optionally include the following parameters: time, ourkey, and uri. For detailed explanations of these fields, refer to the previous document Explanation of Fields in the Authentication URL.
In the process of constructing the encrypted string key, you can choose to include one or more of the above parameters and specify their combination order. For example, if you choose $uri$ourkey$time as the combination order, it means:
- The URL request address (
uri) is the starting part; - Followed by the custom encryption key (
ourkey); - And finally, the timestamp (
time).
For example, with the URL http://cdnetworks.com/browse/index.html, an ourkey of cdnetworks, and a time of 202405131620, the generated unencrypted string key will be /browse/index.htmlcdnetworks202405131620.
Signature Parameter Name
This refers to the name of the authentication signature parameter in the URL, which is set to key by default in our system. For example, in Mode C it’s:
http://domain/uri?key=signature&time=timestamp
You can customize this name as needed. For example, if you set it to cdnwkey, the user can use the query parameter cdnwkey=abc instead of key=abc in the URL to request content from the CDN edge servers.
Timestamp Parameter Name
The refers to the timestamp parameter in the URL, which is named time by default in our system. You can also customize this parameter name as needed. For example, if you set it to cdnwtime, the user can use the query parameter cdnwtime=123 instead of time=123 to represent the timestamp in the URL when requesting content from CDN edge servers.
Valid Time (Seconds)
We offer three methods to configure the valid time for authentication information:
- Upper Limit of Validity Period: Enter a non-negative integer (e.g.,
60) to set the maximum validity period in seconds after thetimefield. For instance, entering60means the authentication information remains valid for one minute following thetimefield in the request URL. - Upper and Lower Limits of Validity Period: Enter two comma-separated values. The first value is the number of seconds before the timestamp (≤0), and the second value is the number of seconds after the timestamp (≥0). For example,
-60,60means the authentication information is valid from one minute before to one minute after the timestamp. - No Validity Period Validation: Enter a minus sign (
-) to disable validity period checks.
Key and Time Positions Interchangeable
By default, in Modes C and D, the positions of the authentication signature and timestamp (key and time parameters) in the URL are fixed and must follow the specified order of the authentication mode. If you set the option to Yes, their positions can be interchangeable.
For example, the following two URLs will be considered authenticated by the CDN edge server, and the content will be served to the client:
http://cdnetworks.com/browse/index.html?key=abc&time=123
http://cdnetworks.com/browse/index.html?time=123&key=abc
Quick Verify if the URL Authentication Configuration is Correct
To avoid errors affecting your online business, it is advisable to initially deploy the configuration to a test environment. Once the configuration is verified as accurate, it can then be officially implemented in the live environment. For details on deploying configurations to a test environment, refer to the tutorial Deploy the Configurations to Staging Environment for Validation.
Additionally, you can use the Timestamp Anti-Hotlinking Calculator available on the CDN console to generate URL authentication parameters and quick verify your configuration. Visit the document Authentication URL Generator for more details.