User-Agent Access Rules
Last update:2025-04-24 11:38:13
When a client sends a request to a web server, it typically carries a User-Agent header, which identifies the device and browser from which the request originates. It details the operating system and version, as well as the browser type and version. Therefore, access control can be performed based on this header. When a CDN edge server receives a client request, it checks the information in the User-Agent field of the HTTP request header, and then allows or denies user requests that comply with specific rules.
The User-Agent acess rule is suitable for the following scenarios:
- When the content is only allowed to be accessed by specific browsers, such as only allowing Internet Explorer to access and denying access from Chrome, User-Agent anti-theft can be used.
- When accelerated domains are only allowed to be accessed by specific clients, such as having a dedicated client that carries specific User-Agent information when sending requests, the User-Agent acess rules can be used.
How to Set Up the User-Agent Access Rule
- Log in to the CDNetworks Console and select the appropriate product.
- Go to the Configuration, locate the domain you wish to configure, and click Edit Configuration
 .
. - Navigate to Hotlink Protection - UA Header Anti-hotlinking in the left sidebar and click Add.
- Configure the settings as follows based on your needs.

Effective Range
This defines the range of requests that User-Agent rules will apply to. You can choose from the following options:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| All Requests | The access control rule applies to all types of requests. |
| Only Homepage | Applies only to the root directory of the domain, such as http://domain/ or https://domain/. |
| Specified File Type | Applies only to specific types of files. You can select from the predefined file types on the left or define custom file types. Separate multiple custom types with a semicolon ;.(e.g., jpg;png). |
| Specified URI | Applies only to requests for content at a specific URI. Two URI matching options are available:Exact matching: Complete URI, including parameters.(e.g., path/index.html?abc=123). Ignore the parameter matching: URI without query parameters.(e.g., path/index.html). |
| Specified Directory | Applies to requests under specific directories. For example, /file/abc/ applies to all content under http://domain/file/abc/*.Note: Directories must start and end with /, and can only contain letters, numbers, and certain special characters (underscore, hyphen, percent sign, dot). Multiple directories are supposed to be seperated with line breaks. |
| URL Pattern | Uses regular expressions to control the range of requests that the rules will be applied to. For example, the pattern *.jpg$ ensures that access control applies to all URLs ending with .jpg. |
Advanced Range Settings
As shown above, you can further refine the rule’s effective range using Advanced Range Settings. This will intersect with the basic effective range for precise control. Select one or more parameters to form an AND relationship with the basic effective range to target specific requests or responses.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Region or Exception Region | Supports direct search selection from the list of countries/regions provided by CDNetworks; For Mainland China, it is possible to select specific provinces or larger geographical areas, such as East China, Southwest China. |
| Exception File Types | Excludes certain file types. Separate multiple types with ;. |
| Exceptional Custom File Types | Excludes custom file types as needed. Separate multiple types with ;. |
| Exception Directory | Excludes specific directory paths. Paths must start and end with /. Separate multiple directories with ;. |
| Exception URL (Regex) | Excludes URLs using regex, e.g., .*\.jpg$. |
| Request Method | Matches HTTP request methods. Separate multiple methods with ;, e.g., GET;POST. |
| Exception Request Method | Excludes specific HTTP request methods. |
User-Agent Type
You can set up either a User-Agent blacklist or whitelist:
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| User-Agent Blacklist | If the User-Agent in the HTTP request header matches the blacklist, the access will be denied for user. |
| User-Agent Whitelist | Users are only allowed access to the content if the User-Agent in their HTTP request header matches the whitelist. |
Tips
Both the User-Agent blacklist and whitelist can contain multiple values, which should be separated by line breaks.
The system supports only one whitelist rule. If multiple User-Agent values are needed, they must all be included within this single whitelist.
Action
When the User-Agent does not meet the set rules, and a request is denied by the CDN, choose whether to return an error code directly or redirect to another URL:
- Deny Access: Returns a 403 error for failed access validations.
- Redirect URL: Redirects failed validations to a specified URL.
Ignore Case
You can set whether the blacklist or whitelist rules are case-sensitive. If set to Yes, the values in the list will NOT be case-sensitive. For example, if Chrome/123.0.0.0 is allowed in the whitelist, the request will be permitted whether the User-Agent is Chrome/123.0.0.0 or chrome/123.0.0.0.
Priority
When multiple access control rules are configured, the CDN prioritizes them based on their numerical value, executing higher numbers first.
After you have completed setting the configurations, please click OK and then select Next to submit your settings. To minimize any potential disruptions to your production environment, we strongly recommend conducting a Pre-deploy test in a staging environment. This crucial step ensures that your configurations are accurate before they go live. Once you have verified the accuracy of the settings, click Deploy Now to implement them in the live environment. The configurations typically become effective within 3-5 minutes.
For comprehensive guidance on pre-deployment testing and to verify the effectiveness of your configurations, please consult the tutorial Deploy the Configurations to Staging Environment for Validation.
Notes
Please DO NOT configure both User-Agent blacklists and whitelists simultaneously, as this may result in all CDN access being denied, potentially disrupting your online operations. For instance, configuring both a User-Agent blacklist and whitelist as shown below can lead to all access being denied.
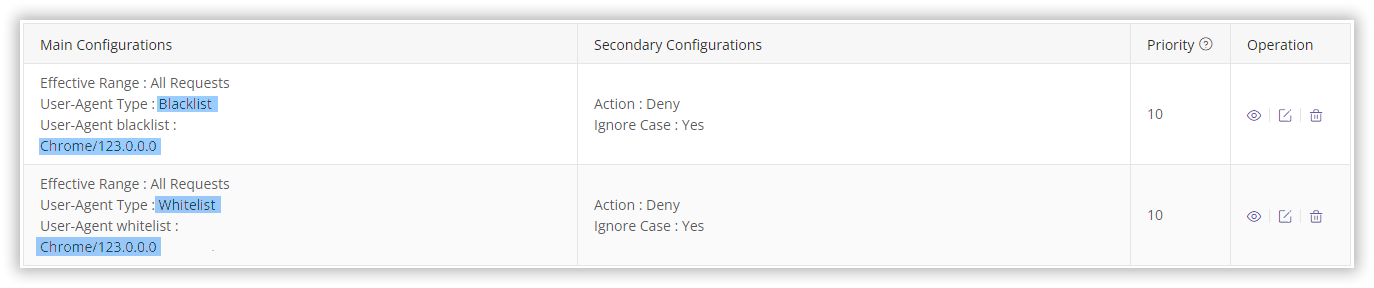
Why would all access be denied?
- Access is denied when the request’s User-Agent carries the value
Chrome/123.0.0.0, as it matches the User-Agent blacklist. - Conversely, Requests without the User-Agent
Chrome/123.0.0.0, while not denied by the blacklist, fail to meet the whitelist (which only allows access for requests with the User-AgentChrome/123.0.0.0) and are also denied.
If you need to configure both a blacklist and a whitelist, please contact our Customer Service for assistance to ensure proper setup.