IAM policy Setting
Last update:2025-08-18 15:58:52
In this chapter, we will introduce how to configure policies through examples to help you better understand the practical application scenarios of policies.
Policy Types
1. System Policies
| Policy Name | Permission Scope | Function Description |
|---|---|---|
| CDNWCloudWOSReadOnlyAccess | All WOS Resources (Object Storage) | Read-Only Access: Provides read access to all resources in WOS (Object Storage) |
| CDNWCloudWOSResourceCreatorAccess | WOS Resources Created by User | Full Management Access: Grants full operational permissions only to the storage spaces and content created by the user |
| CDNWCloudWOSFullAccess | All WOS Resources (Object Storage) | Super Administrator Access: Grants full access over all resources in WOS(Object Storage) |
Note: System will use the smaller/smallest policy when you grant multiple system policies to sub accounts. If you want to grant FullAccess permission, please just authorize
CDNWCloudWOSFullAccessonly.
2. Custom Policies
A custom policy is a user-defined permission control policy used for more refined management of resource access permissions in the Identity and Access Management (IAM) system. Unlike system-defined policies, custom policies allow users to set permission rules according to specific business needs.
Configuring Permission Policies in the Console
Configuring System Policies
- Log in to the CDNetworks Console and click on your account avatar to find IAM.
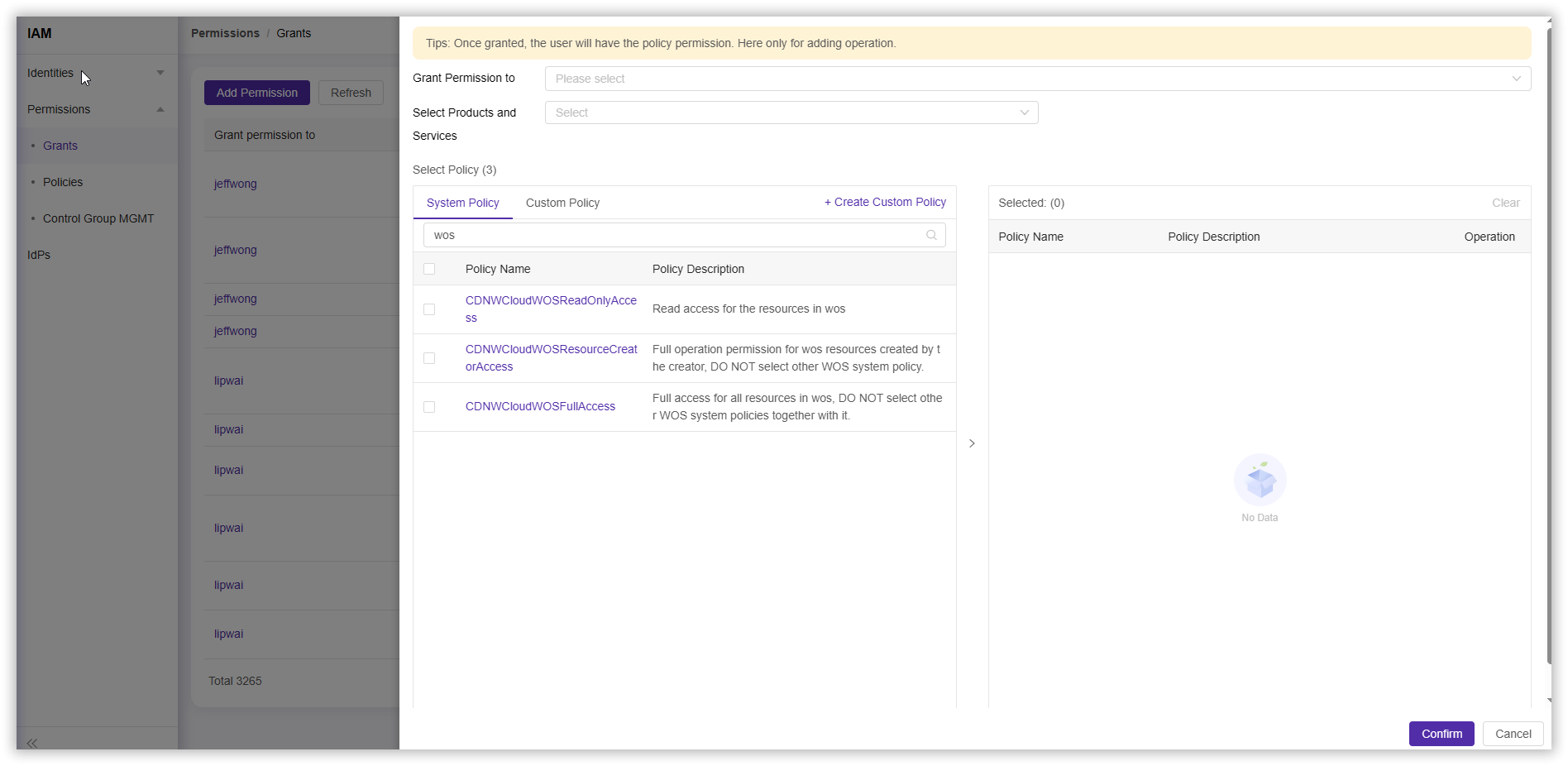
- Click Permission > Grants > Add Permission, search for “WOS” in the policy selection section, choose the System Policy you want to configure, and complete other configurations according to your needs.
Configuring Custom Policies
Create a New Policy Using Visual Configuration
- Log in to the CDNetworks Console and click on your account avatar to find IAM.
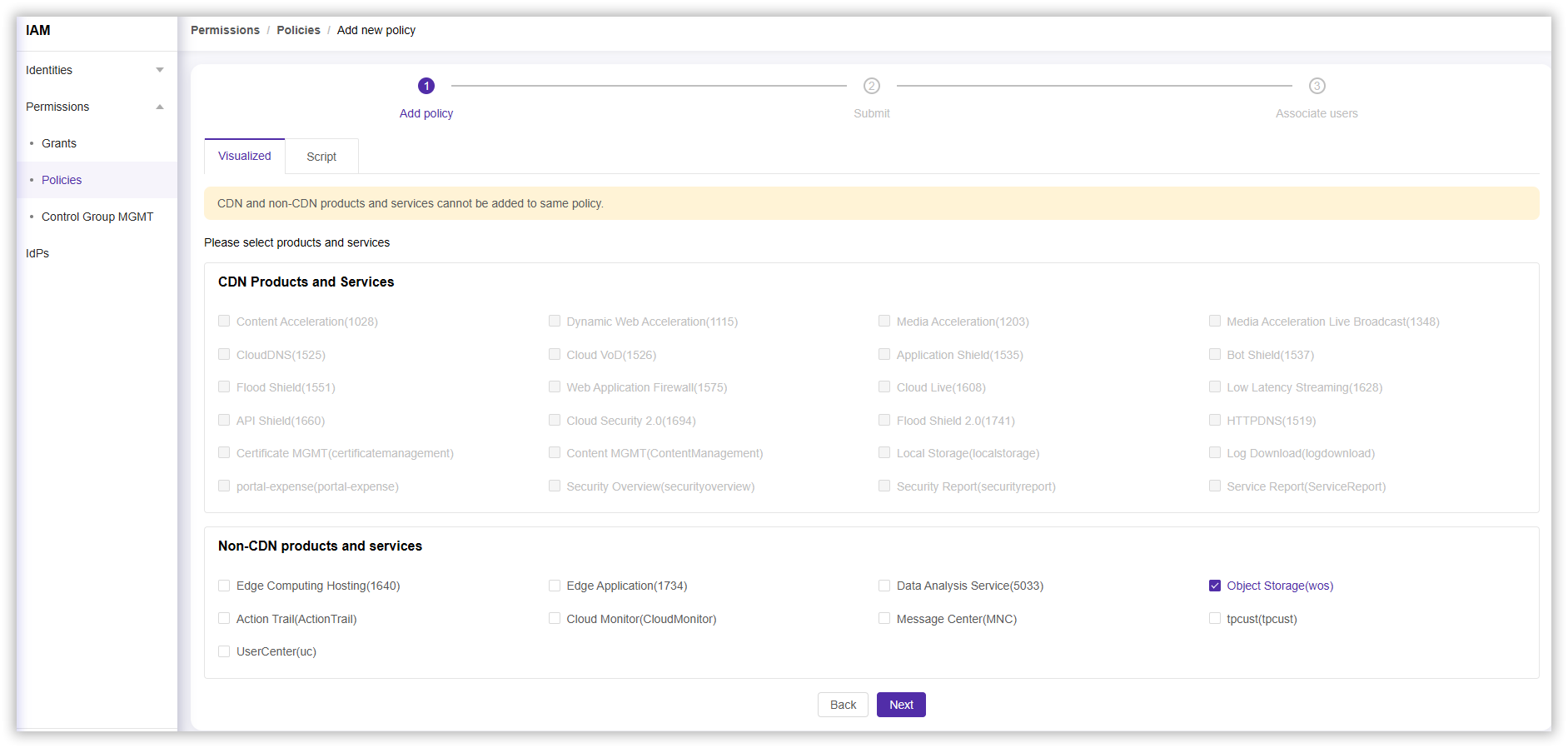
- Click Permission > Policies > Add Policy, then select Visualized in the Create Policy section.
- In the Non-CDN Products and Services section, click Object Storage (wos), then select Next.
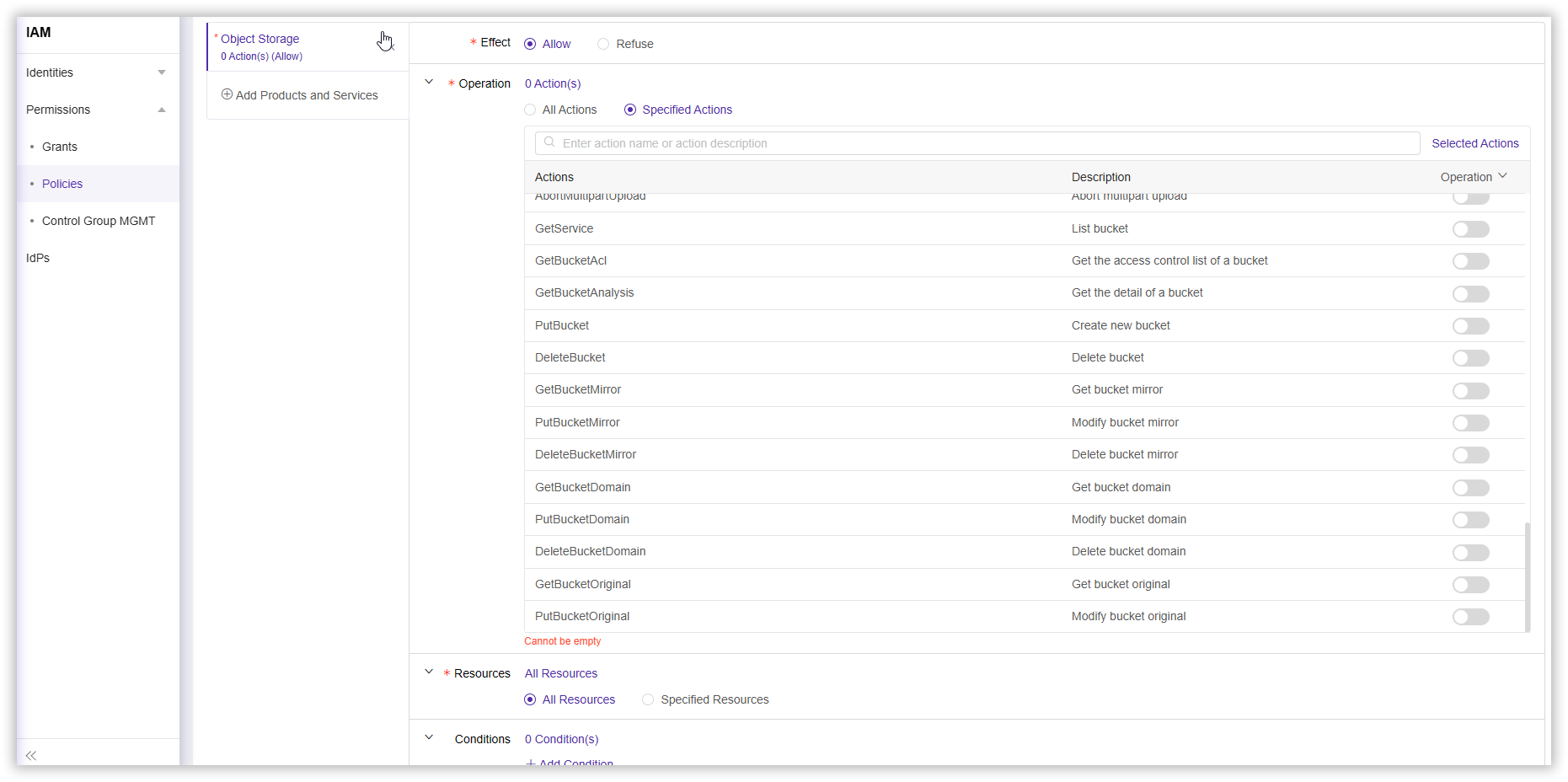
- Complete other configurations according to your needs and select Next.
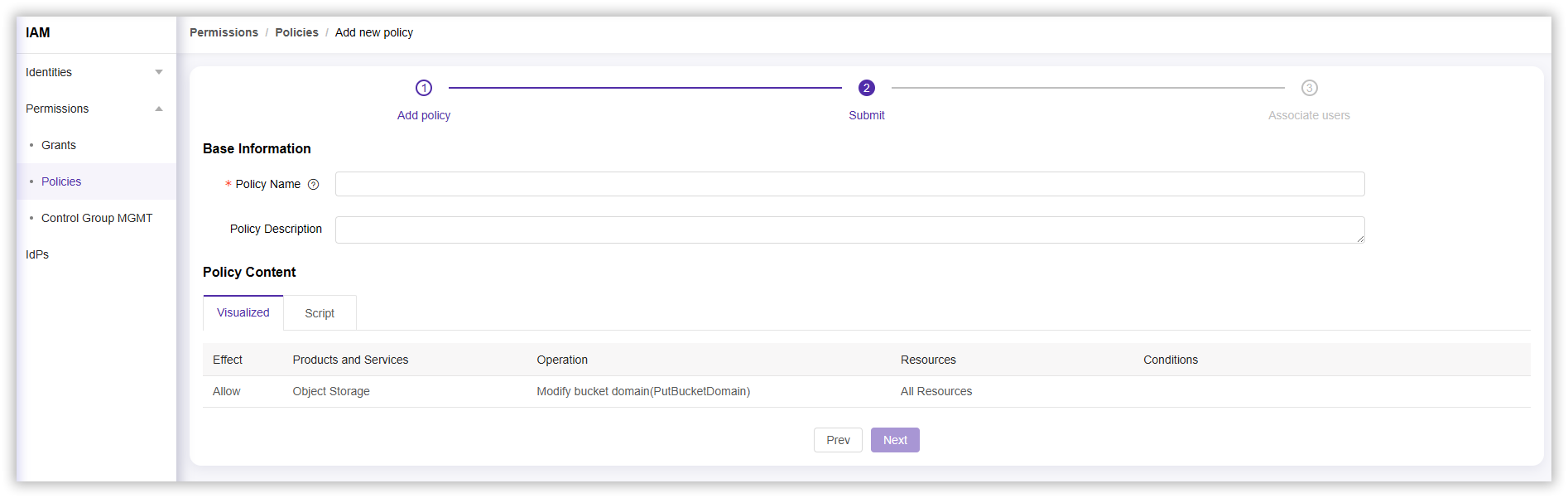
- In the completion policy section, enter a Policy Name (required) and Policy Description, then select Next to complete the policy creation.
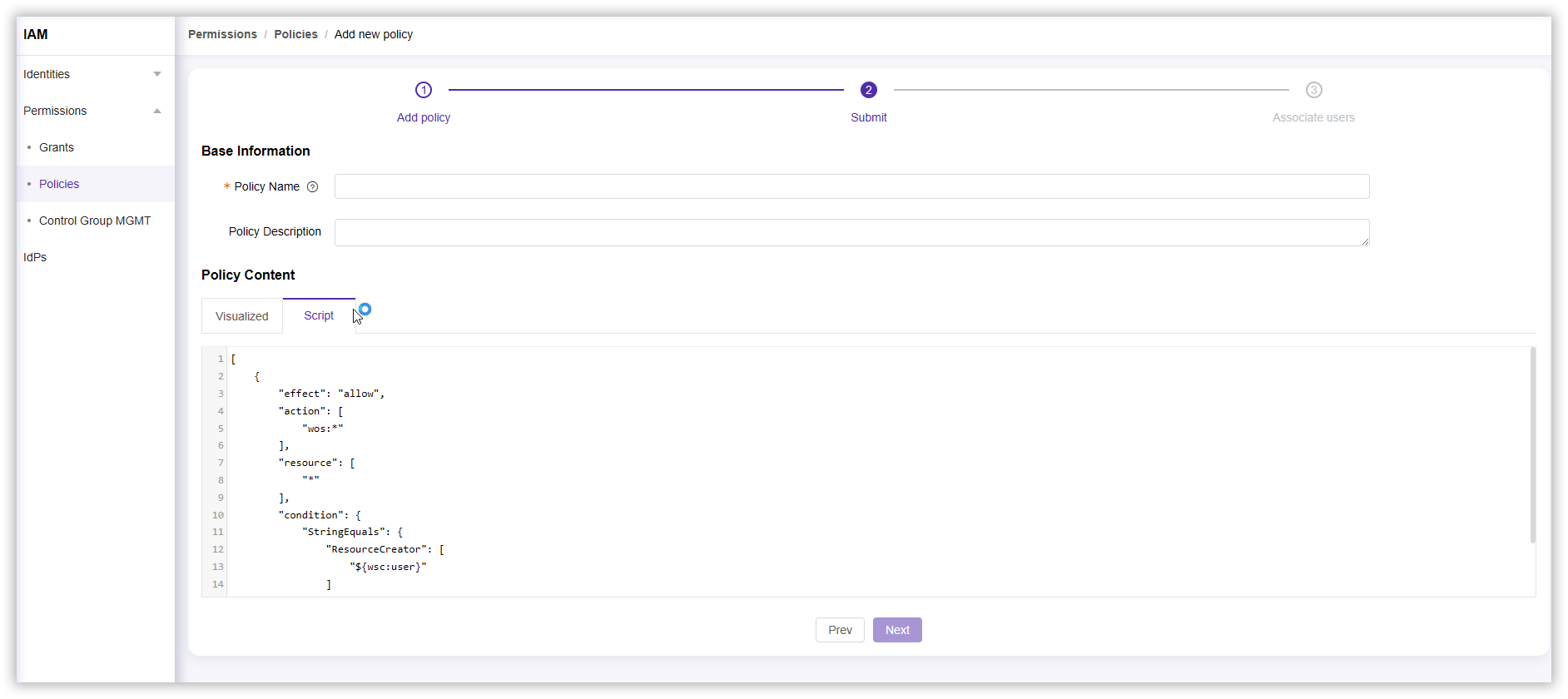
Create a New Policy Using Script
- Log in to the CDNetworks Console and click on your account avatar to find IAM.
- Click Permission > Policies > Add Policy, and select Script in the Create Policy section.
- Complete the script configuration according to your needs and select Next.
- In the completion policy section, enter a Policy Name (required) and Policy Description, then select Next to complete the policy creation.
Configure Custom Policies
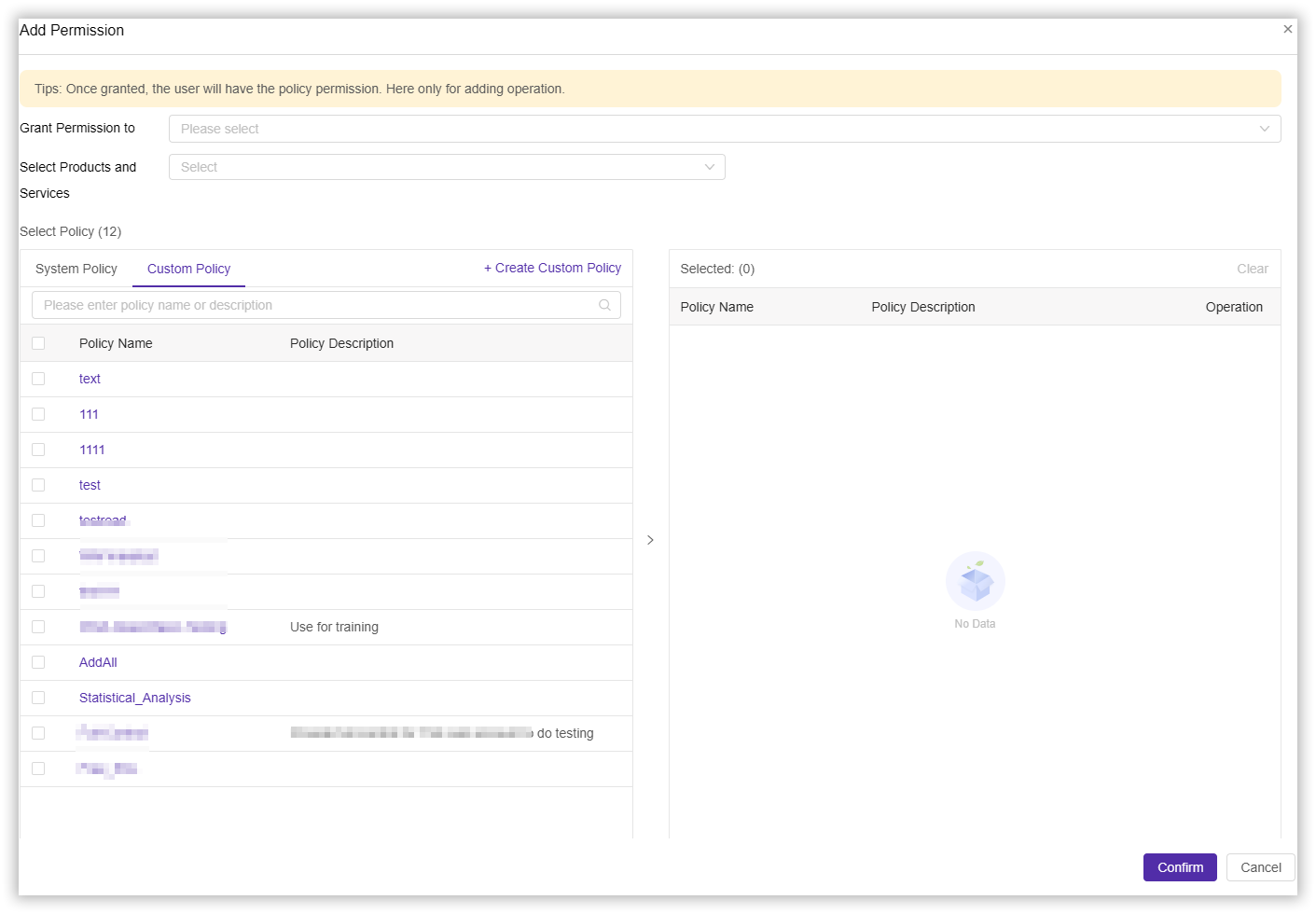
After creating a new custom policy, you can authorize the custom policy to specified users.
- Log in to the CDNetworks Console and click on your account avatar to find IAM.
- Click Permission > Grants > Add Permission, click on your created Custom Policy in the policy selection section, and complete other configurations according to your needs.
Script Policy Examples
Example 1: Access to the list of spaces
An example of the authorization policy created is as follows:
{
"version": "1",
"statement": [{
"effect": "allow",
"action": ["wos:GetService"],
"resource": ["wsc:wos:*:*:*"]
}]
}
Note: To use the sub-account of the console, you need to have the permission to obtain the space list, otherwise you may not be able to use other operations on the console normally.***
Example 2: Fully manage the permissions of a bucket
Suppose the bucket name is “testbucket”. Then the authorization policy created is as follows:
{
"version": "1",
"statement": [
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": ["wos:*"],
"resource": [
"wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket",
"wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket/*"
]
}
]
}
Example 3: Permission to operate a bucket resource
Assuming the bucket name is “testbucket”, the authorization policy created is as follows:
{
"version": "1",
"statement": [
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": ["wos:GetBucket"],
"resource": ["wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket"]
},
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": [
"wos:PutObject",
"wos:GetObject",
"wos:DeleteObject",
"wos:AbortMultipartUpload",
"wos:ListParts"
]
"resource": [
"wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket/*"
]
}
]
}
Example 4: WOS directory level permissions
Assuming the bucket name is “testbucket”, there are some directories under this bucket, namely photo, video, and music; each directory has a category directory. The directory tree structure is as follows:
testbucket (space)
├── photo
│ ├── 2017
│ └── 2018
├── video
│ ├── 2016
│ ├── 2017
│ └── 2018 // Grant this directory read-only permission
└── music
├── 2017
└── 2018
Suppose we need to authorize a sub-account to have read-only access to the testbucket/video/2018/ directory. Two scenarios are introduced below.
Scenario 1: The sub-account knows the path of the file and only needs the permission to read the content of the file, not the permission to list the file.
The feature of this scenario is that the sub-account knows the full path of the file and can use the complete file path to read it directly document content. Usually we will grant such authority to a software system, and the file path in the system conforms to a certain rule (for example, the file name is an employee ID).
{
"version": "1",
"statement": [
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": [
"wos:GetObject"
],
"resource": [
"wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket/video/2018/*"
]
}
]
}
Scenario 2: The sub-account uses the object storage console to access the directory testbucket/video/2018/ and
needs to create the following permissions:
- List all bucket permissions
- View the permissions of all resources under testbucket
- Permission to operate resources under testbucket/video/2018
{
"version": "1",
"statement": [
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": [
"wos:GetService"
],
"resource": [
"wsc:wos:*:*:*"
]
},
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": [
"wos:GetBucket"
],
"resource": [
"wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket"
]
},
{
"effect": "allow",
"action": [
"wos:PutObject",
"wos:DeleteObject",
"wos:PutFolder",
"wos:PutMediaOperation"
],
"resource": [
"wsc:wos:*:*:testbucket/video/2018/*"
]
}
]
}
Example 5: ccess to view statistical analysis
An example of the authorization policy created is as follows:
{
"version": "1",
"statement": [{
"action": ["wos:GetBucketAnalysis"],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": ["wsc:wos:*:*:*"]
}]
}